Is Nuclear Envelope In Plant And Animal Cells
Nuclear Membrane Definition
"Nuclear membrane is a double-layered membrane that separates the contents of the nucleus from the remainder of the cell."
What is the Nuclear Membrane?
All the eukaryotic cells that are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists have a control centre, called a nucleus where DNA is stored. Every nucleus is girdled and covered by a double-layered membrane, known as the nuclear envelope or nuclear membrane. Information technology separates the nucleoplasm (the fluid present in the nucleus), from the cytoplasm .
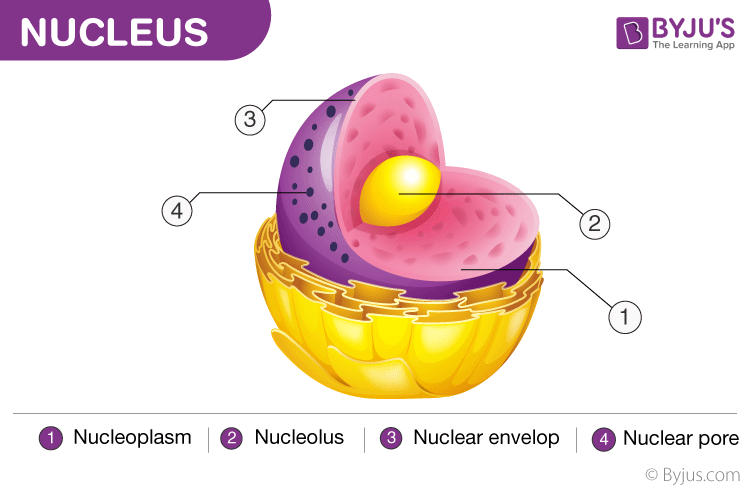
The nuclear envelope is also called nuclear membrane. It is made up of ii lipid bilayer membranes
The nuclear membrane is present in both the found and animal cells. Cells carry out a multitude of functions such as poly peptide building, conversion of molecules into energy and emptying of unnecessary products.
This membrane guards the genetic cloth of the cells against the exterior of the nucleus where chemic reactions are taking identify. Also, information technology carries several proteins which are crucial in the arrangement of DNA and to control genes.
Nuclear Membrane Construction
A nuclear membrane is composed upwardly of two membranes – an inner and an outer membrane. Both membranes consist of phospholipids that are organized in a bilayer. The complete nuclear membrane includes 4 series of phospholipids.
The perinuclear space separates the outer and inner membrane. The outer membrane works by the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It is an organelle which is important in the transportation of proteins.
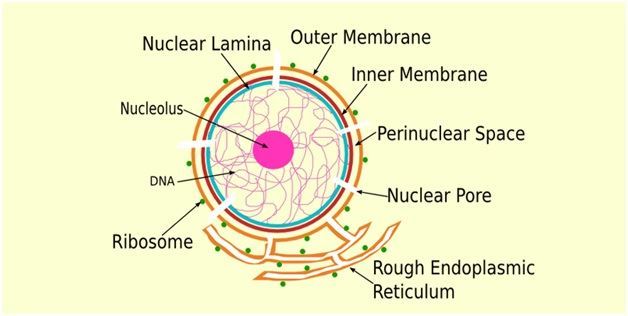
Nuclear Membrane Structure
The outer membrane and the rough endoplasmic reticulum both are covered in ribosomes as these are the true location of protein production.
On the nucleoplasm, nuclear lamina is connected to the inner nuclear membrane. The nuclear lamina also attaches to and secures chromatin which is organized loosely in protein structure and DNA. A protein layer gives back up and forcefulness to the nuclear membrane.
Also Read:The Nucleus
Parts Of Nuclear Membrane
The nuclear membrane encloses the prison cell nucleus and consists of the post-obit parts:
Outer Membrane
It is a lipid bilayer containing ii layers of molecules of lipid. The outer layer is made upwards of lipids which have ribosomes on the surface that are linked to the endoplasmic reticulum.
Inner Membrane
It contains proteins that rearrange the nucleus and chain the genetic fabric in position. The nuclear lamina is the attachment of proteins and fibres that are linked to the inner membrane. It provides structural support to the nucleus, assists in Dna repair, controls cell bike events such as prison cell division and also on Deoxyribonucleic acid replication.
Nuclear Pores
They move through both the inner and outer membranes of the nuclear membrane and are composed of large complex proteins which allow a few molecules to permeate by the nuclear envelope. Each of the nuclear pores consists of 30 distinct proteins which operate together to transfer materials. Also, they link the inner and outer membranes.
Nucleolus
These are tiny spherical bodies that are situated in the nucleus as they are unremarkably present in a centralized site only are typically found closer to the nuclear membrane. What sets them apart from other nuclear material is that they are built past the (NOR)nucleolus organizing region of chromosomes, which is known to store the genes that are necessary for full ribosomal production. They encode ribosomal RNA subunits.
Nucleoplasm
Nucleoplasm is a remarkably viscous liquid that contains the nuclear hyaloplasm which is the more soluble and liquid portion of the nucleoplasm. It is a type of protoplasm that is similar to the cytoplasm, which is present throughout the prison cell body to the exterior of the nucleus.
As specific functions are carried out inside the nucleus, a unlike type of protoplasm is required. The constituents of the nucleoplasm are water, dissolved ions, and a blend of other substances. This chemical element is completely confined in the nuclear envelope containing nucleotides and crucial enzymes that promote replication.
As well Read:Nucleoplasm
Nuclear Membrane Function
Following are the important functions of the nuclear membrane:
- The nuclear envelope has tiny holes which are identified equally nuclear pores. The pores enable the content to menstruum in and out of the nucleus. Information technology likewise connects the outer membrane and the inner membrane.
- The nuclear envelope's surface surface area extends and doubles the nuclear pores during the interphase part of jail cell division.
- Nuclear membrane shields the nucleus with a double membrane by many pores that assistance in controlling the crossing of macromolecules such as proteins and RNA and let costless passage of water, ions, ATP and pocket-size molecules. The membrane controls the flow of information in the cell as it is conducted by the macromolecules.
Also Read: Nucleolus
Function Of Nucleus
The nucleus is a double-membrane bound cell organelle that is located in the eukaryotic cells and composes of the cell'south genetic cloth – the Dna. Since it maintains the integrity of the genes that command the factor expression hence controlling the cell's activities, information technology is known as the command centre of the cell.
The following are the dissimilar roles of the nucleus:
- It is responsible for regulating the heredity traits of an entity
- It controls protein synthesis, growth, cell division, and differentiation
- It reserves heredity material in the course of DNA strands that besides store RNA and proteins in the nucleolus
- It is a section for the process of transcription wherein mRNA is produced to generate proteins
- Assists in the exchange of RNA and DNA betwixt the cell and the nucleus
- The nucleolus generates ribosomes that are referred to every bit protein factories
- It controls the integrity of gene expression and genes
Difference Between Nuclear Membrane in Plant and Animal Cells
The deviation between the nuclear membrane in plant and creature cells are as follows:
| Nuclear Membrane in Plant Jail cell | Nuclear Membrane in Brute Cell |
| They lack several proteins. | They possess proteins. |
| The centrosome is absent. | The centrosome is present. |
To learn more near nuclear membrane, its structure and function keep visiting BYJU'S Biology or download BYJU'S app for farther reference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main part of the nuclear membrane?
The nuclear membrane encloses the DNA inside the nucleus and protects it from the substances in the cytoplasm. It also regulates the entry and exit of substances in the nucleus.
How does the nuclear membrane appear like?
The nuclear membrane is fabricated up of ii lipid bilayer membranes that environs the nucleus containing the genetic material. The inner membrane and the outer membrane are separated by perinuclear space.
What is the departure betwixt the prison cell membrane and the nuclear membrane?
The cell membrane is the lipid bilayer surrounding the entire cell. The nuclear membrane, on the other hand, surrounds the nucleus. The cell membrane is in the class of a continuous sheet. On the opposite, the nuclear membrane is not a continuous canvass simply is made of a serial of vesicles that come up together to enclose the nucleus.
Why does the nuclear envelope intermission during mitosis?
During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks to let the mitotic spindle fibres to attach to the chromosomes.
What would happen if the nucleus had no membrane?
The nuclear membrane provides proper shape to the nucleus and ensures that the cytoplasm does not leak into the nucleus. If the nuclear membrane was absent-minded, the molecules in the cytoplasm would enter into the nucleus and destroy a part of the DNA. This would impair the operation of the jail cell and would lead to cell death.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/nuclear-membrane/
Posted by: hansontruckly.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is Nuclear Envelope In Plant And Animal Cells"
Post a Comment